Future Earth
R&D Focus Area: Human-Information Technology Ecosystem
- Legal being: electronic personhoods of artificial intelligence and robots in NAJIMI society, based on a reconsideration of the concept of autonomy
- Co-Creation and Communication for Real-Time Technology Assessment (CoRTTA) on Information Technology and Molecular Robotics / Co-creation of Molecular Robot ELSI and Real-time Technology Assessment Research
R&D Focus Area: Creating a Safe and Secure Living Environment in the Changing Public and Private Spheres
R&D Program: Science of Science, Technology and Innovation Policy
R&D Focus Area: Designing a Sustainable Society through Intergenerational Co-creation
R&D Focus Area: Creating Community-based Robust and Resilient Society
R&D Focus Area: Redesigning Communities for Aged Society
- Construction of an "easy" and "pleasant" agricultural management style to suit each locality
- For "ease of use", elderly people/companies/researchers collaborate in the "Everybody Lab"
- A system to watch over elderly people by "telephone" was developed and disseminated; to be featured in elementary school textbooks as well
R&D Focus Area: Protecting Children from Crime
- Establishing an Empirical Basis to Measure and Prevent Crimes against Children
- Training Program for Video Recorded Interview (Forensic interviews) with Children in Forensic Context
- Development of Support Systems for Community Safety Planning
- Development of Advanced Information and Simulation Technology for Intentional Injury Prevention
R&D Focus Area: Science Technology and Humanity
- Establishment of the "Science Media Centre of Japan" as an Information Hub for Science and Technology
- Construction of a Pragmatic Scientist Community Contributing to the Stakeholder-driven Management of the Local Environment
- The Nagahama Rules for Genome Epidemiology Studies Open to the Community
- Legal Decision-making under Scientific Uncertainty
R&D Focus Area "Brain-Science and Society"
- Identification of Factors Affecting Cognitive and Behavioral Development of Children in Japan Based on a Cohort Study; Japan Children's Study
- R&D Program: Brain-Science and Education Type Ⅱ
- R&D in development of prefrontal cortex functions development and improvement systems
- Elucidation of brain mechanisms of learning difficulties and development and evaluation of educational support programs
R&D Focus Area: Information Technology and Society
R&D Focus Area: Social System & Social Technology Theory
R&D Focus Area: Sustainable Society
R&D Focus Area: Safety and Security
Implementation-Support Program
- Co-creating Communities for Aged Society
- Long-Standing Tsunami Response and Education Activities Result in "Miracle of Kamaishi"
- Community-based System for Early Identification and Intervention of Toddlers with Autism Spectrum Disorder, whose Item Incorporated in Maternal and Child Health Handbook
- Development of Predictive System to Prevent Trailer Truck Rollover
- Development and Introduction of Systems for Providing Life Recovery Support Measures Rapidly and Fairly after a Major Disaster
- Microbubbles Clean Seawater, Bringing Hope to Aquaculture Producers in the Tsunami Zone
- Development and Deployment of Web System to Support Children and Their Parents Contributes to the Quality Improvement of Childcare Professionals
- A joystick system to enable people with disabled limbs to drive a car
- Practical Utilization of Multi-dimensional Scale for PDD and ADHD (MSPA) across the Medical, Education and Social field
R&D Focus Area: Human-Information Technology Ecosystem
Legal being: electronic personhoods of artificial intelligence and robots in NAJIMI society, based on a reconsideration of the concept of autonomy
Principal Investigator: ASADA Minoru (Professor, Institute for Open and Transdisciplinary Research Initiatives, Osaka University)

This project examined the legal implications in the event of an accident caused by artificial intelligence, highlighted the limitations of the current legal system and devised a new institutional model that would not impede technological advances such as mandating the improvement of companies and developers instead of punishment. By hosting workshops on cooperation with the technology development side and dialogue with the general public and ascertaining and making improvements to the effectiveness of the proposed model, This project proposed solutions to the relationship between artificial intelligence and the law and that we believe will held realize a society that can coexist with technology.
Co-Creation and Communication for Real-Time Technology Assessment (CoRTTA) on Information Technology and Molecular Robotics
Principal Investigator: SHINEHA Ryuuma (Associate Professor, Research Center on Ethical, Legal, and Social Issues (ELSI), Osaka University)
Co-creation of Molecular Robot ELSI and Real-time Technology Assessment Research
Principal Investigator: KONAGAYA Akihiko, (Visiting Professor, Faculty of Humanities, Keisen University)
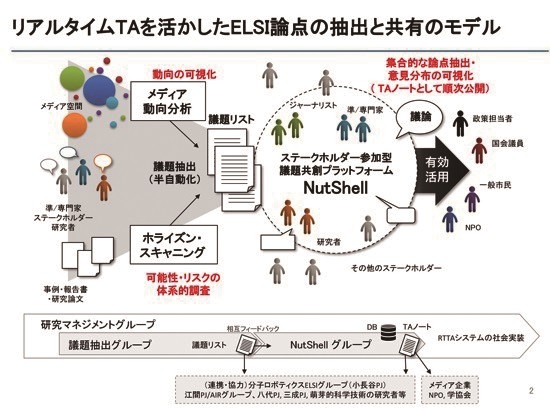
ELSI and RRI issues that may involve molecular robots in the future have been organized based on past case studies of similar technologies and compiled as TA (Technology Assessment) notes. Through collaboration between the Molecular Robot Ethics Study Group and the Molecular Robotics Annual Meeting, this project promote mutual understanding between humanities and social sciences researchers and molecular robotics researchers and obtain feedback on the activities of both. This project is continually discussing the formulation of molecular robotics guidelines, and these efforts are expected to create a society where molecular robot technology and humans are familiarized.
R&D Focus Area: Creating a Safe and Secure Living Environment in the Changing Public and Private Spheres
Reducing online risks for minors with the help of a system that detects users who commit premeditated online grooming: FY2017-FY2021
Principal Investigator: TORIUMI Fujio (Professor, School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo)

To reduce online risks for minors, the R&D project developed an online risk detection system using an algorithm based on non-linguistic information while considering the secrecy of personal information and communications, enabling the detection of users who commit premeditated online grooming. Introducing this system to social networking services (SNS) used among minors prevented this type of risk, with SNS providers having already applied it to their systems. In addition, the R&D project produced worksheets, cartoons, and other educational materials to make minors aware of this online risk and manuals for use by teachers. With this system covered by newspapers and other media, we are spreading its R&D results and further field utilization.
The development of an application named "Sodatsu WA" helps prevent child abuse and domestic violence (DV) even during pregnancy: FY2016-FY2020
Principal Investigator: FUJIWARA Takeo (Professor, Global Health Promotion, Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU))
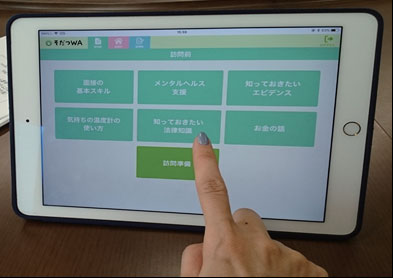
Aiming to prevent child abuse and DV, the R&D project developed "Sodatsu WA," an application to support public health nurses by utilizing pregnancy notifications. The system is provided with convenient support content and functions needed when a public health nurse visits the homes of pregnant women, with the demonstration field (the health center in Adachi-ku, Tokyo) continuing the use of this system today. In addition, the application also provides a set of learning materials (text and audio) describing how to approach pregnant women reluctant to receive support or how to support pregnant women who suffer from mental health problems. For this reason, this system is spreading to educate public health nurses and at midwife outpatient clinics of maternity hospitals too.
R&D Program: Science of Science, Technology and Innovation Policy
Economic Growth Analysis of Science, Technology, and Innovation Policies: FY2012-2015
Principal Investigator: NIREI Makoto (Associate Professor, Institute of Innovation Research, Hitotsubashi University)
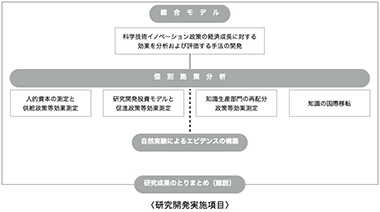
We developed methods for analyzing and evaluating the effects of science and technology innovation policies on economic growth, conducted an economic analysis based on a theory regarding important individual policy areas (knowledge production, manpower supply, R&D investment and international knowledge transfer), and broadly provided analysis and evaluation methods, data and basic estimated results to policymakers. As a result, these were then used in the actual policy formation process, such as the revision of the System of National Accounts carried out by the Cabinet Office, the construction of R&D capital statistics, and the establishment of the 5th Science and Technology Basic Plan.
Future Earth
Transdisciplinary Study of Natural Resource Management under Poverty Conditions Collaborating with Vulnerable Sectors: FY2017-2019
Principal Investigator: SATO Tetsu (Professor, Ehime University Faculty of Collaborative Regional Innovation)

In the total of 9 regions across 6 countries, including Indonesia and Malawi, while working together with resident researchers and local NGOs, we developed and demonstrated a mechanism that leads to the improvement of life in poverty and welfare by extracting and visualizing the wisdom (intrinsic innovation) of people living in poverty based on the challenges they face and the knowledge they possess, and applying it to sustainable management and effective utilization of natural resources. Because this method is a common approach to people with disabilities, those facing economic hardship and others with various issues, we expect it to be applied to similar situations in other communities and areas.
R&D Focus Area: Designing a Sustainable Society through Intergenerational Co-creation
Ensuring Sustainability at Local Government Level through Promoting Implementation of Multigenerational Participatory Stock Management Methods: FY2014-2019
Principal Investigator: KURASAKA Hidefumi (Professor, Graduate School of Social Sciences, Chiba University)

With local municipalities facing declining populations and shrinking finances, we developed the "Future Chart" that simulates approximately 10 areas of local administrations including changes in the industrial structure and the prospect of maintenance and management of public facilities, roadways and farmland, and displays those transitions every five years with a graph, based on various statistical data for each of the 1,741 municipalities in Japan. In addition, we developed methods such as the "Future Workshop" to create scenarios that should be considered based on future forecasts with multi-generational participation. The Future Chart issuing program, which was released for free in October 2017, was well received and downloaded more than 20,000 times. The Future Workshop was also widely utilized in communities other than those collaborated in this project, and as a part of integrated study activities at junior high and high schools.
Distributed Rainwater Management for a Sustainable Well-being Society: FY2015-2019
Principal Investigator: SHIMATANI Yukihiro (Professor, Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University)
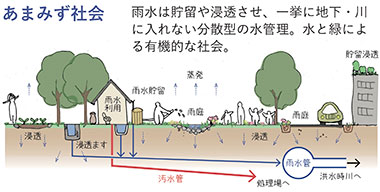
To solve the issues of the current centralized water management system, we proposed an urban vision under the name of "Amamizu Society" (Rainfall Society) by focusing on the Hii River area basin in Fukuoka City, which has experienced frequent flooding in recent years, and developed a method for a decentralized water management system that uses intergenerational co-creation to store and penetrate water in all areas of the basin while creating higher-quality greenery. This method was deployed at Tokyo's Zenpukuji River area and other locations, and is gaining international attention not only for its effectiveness in terms of disaster prevention, but also because it enriches the local ecosystem, increases cultural value, and helps to revitalize communities. We have already collaborated with JICA projects, the World Bank and Ramsar Center Japan, and expect that this method will spread both in Japan and abroad in a self-directed manner.
Restoring a Beautiful and Rich Inner Bay through "Fish Local, Eat Local": FY2016-2019
Principal Investigator: OTSUKA Koji (Professor, Graduate School of Humanities and Sustainable System Sciences, Osaka Prefecture University)

In Osaka Bay's Hannan City, the sustainability of the fishing industry is threatened by declining fish hauls, a declining habit of fish-eating among young people, and the aging and decreasing number of fishers. We chose the city as a model area, and created a sustainable model that covers a series of processes including production, fish haul, distribution and consumption as a whole and developed a comprehensive evaluation method that integrated environmental, economic and social aspects. Obtaining the participation of various stakeholders from multiple generations, the project implemented multifaceted initiatives such as improving fishing ground environments using recycled fish scraps, achieving oyster farming through cocreation with fishing cooperatives, developing new distribution methods for fisheries products using information technology, holding events for children to promote fisheating, and conducting trial internet sales. We expect the project to expand throughout the entire Osaka Bay area in the future.
R&D Focus Area: R&D Focus Area: Creating Community-based Robust and Resilient Society
The community resilience theory was corroborated through the support of collective relocation from the disaster-stricken area
(Redevelopment of Tsunami Impacted Coastal Region to Save Life and to Implement Disaster Resilient Community: FY2012-2015/ Community-Based Reconstruction and Recovery of Cultural Landscape After the Kumamoto Earthquakes: FY2017-2018)
Principal Investigator: ISHIKAWA Mikiko (Professor, Human General Science and Engineering Section, Faculty of Science and Engineering, Chuo University)

The Sennan Alluvial Plain including the Tamaura District of Iwanuma City, Miyagi Prefecture sustained great damage from the Great East Japan Earthquake. We corroborated to develop a method concerning the path of reconstruction or formulation of urban/local plans while supporting the collective relocation therefrom. Our addressing of the revitalization of the "Coastal Region to Protect Life" that proceeded, while carefully gathering each of the resident's opinions, was broadcast in several instalments of the NHK Special program and produced a great sensation. Also, our "Suggestions" submitted to the Science Council of Japan went through profound discussion and were disclosed to greatly affect how the reconstruction should be.
Development of Comprehensive Disaster Mitigation Project of "Preservation Districts for Groups of Traditional Buildings": FY2012-2015
Earthquake Recovery in Community-Dependent Historic Towns: FY2016-2017
Principal Investigator: YOKOUCHI Hajime (Associate Professor, Department of Architecture, Oyama National College of Technology)

In the Preservation District for Groups of Traditional Buildings in the northern Kanto region (Kauemon-cho, Tochigi City; Makabe, Sakuragawa City; Kiryu-shinmachi, Kiryu City), where many traditional earthen-walled storehouse style buildings still remain, we created a place to maintain regular ties with various stakeholders utilizing local history and traditional culture, as well as a system to increase the vitality of the region by holding workshops where young people and private organizations revitalize vacant houses and simulate daily lives in the past. We also promoted the establishment of a system to have everyone help to protect the town by developing guidelines for repairs and landscaping from the standpoint of earthquake and fire resistance, creating a construction system to inherit traditional construction methods, creating disaster prevention guidelines with the participation of local residents, and conducting comprehensive disaster prevention drills. The area was damaged by torrential rains that struck the Kanto and Tohoku regions in 2015, but the built "connections" significantly contributed to recovery activities.
R&D Focus Area: Redesigning Communities for Aged Society
Construction of an "easy" and "pleasant" agricultural management style to suit each locality (Innovations in Age-friendly Farming: FY2011-2014)
Principal Investigator: TERAOKA Shingo (Professor, Cultural and Social Science School, Faculty of Letters, Nara Women's University)

We addressed research and development in Shimoichi-Chou, Nara Prefecture, where persimmon agriculture is thriving, for heightening the sustainability of mountainous regions by reviewing how agriculture should be to allow the elderly people to continue working "easily and pleasantly." We gained outcomes from various viewpoints such as the "village inspection method" to sociologically clarify the problems in the locality, method used in persimmon agriculture not to be burdensome to the farmer's bodies, development of electric farm equipment easy for the elderly people to use, body exercises to eliminate the physical problems peculiar to persimmon agriculture, etc. These activities won the 2014 2nd Platinum Award Excellence Award. Also, we were invited to Turkey, a major agricultural country; thus our outcomes are gathering attention widely in Japan and overseas.
For "ease of use", elderly people/companies/researchers collaborate in the "Everybody Lab" (Founding the Center for Usability and Aging Research (CUAR) with senior citizens: FY2011-2014)
Principal Investigator: T.HARADA Etsuko (Professor, Human-Related Psychological Area, University of Tsukuba)

Under the theme "elderly people's 'ease of use'," we started up the "Everybody's Ease of Use Lab (named the Everybody Lab)" as a place of dialogue between elderly people, companies, and researchers. Here elderly people participate in tests and discuss the things or services that companies have brought in through the coordinator. For the elderly people, it is a place of activities where they can make social contributions to thing-making or local networking while, for the companies and researchers, it is a place for deepening their discernment of “ease of use” through dialogue with the elderly people. The Everybody Lab activities are gathering attention abroad as well, e.g., winning the Gold Prize in the IAUD's (International Association for Universal Design) 2014 Award, Social Design Sector.
A system to watch over elderly people by "telephone" was developed and disseminated; to be featured in elementary school textbooks as well (Aging in Place with ICT: FY2010-2013)
Principal Investigator: OGAWA Akiko (Professor, Department of Social Welfare, Iwate Prefectural University)
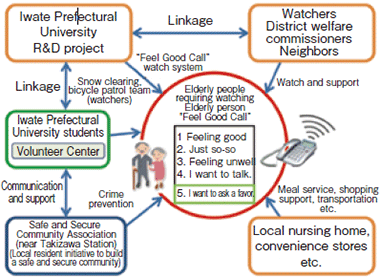
We developed and disseminated a system to enable an old person living alone to communicate when in trouble, etc. casually to the supporter by household telephone, as well as making a community which utilizes the system. The supporter can provide life support in shopping areas, etc. by gently watching over the elderly people in the area in collaboration with the social welfare council or the people in the area, and rush to an old person as alerted in an emergency. The system was introduced to (the then) Takizawa Village, Iwate Prefecture or otherwise utilized in temporary housing after the Great East Japan Earthquake as well. Scenes from these activities have been introduced in textbooks on society for the 5th grade of elementary school since FY2015.
R&D Focus Area: Protecting Children from Crime
Establishing an Empirical Basis to Measure and Prevent Crimes against Children (FY2007-2011)
Principal Investigator: HARADA Yutaka (Director, Department of Criminology and Behavioral Sciences, National Research Institute of Police Science (NRIPS))
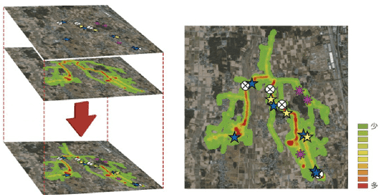
The project developed two 'yardsticks' in order to understand crime risks: a) occurrence of crime affecting children and b) children's daily activities. When the two yardsticks are cross-referenced using GIS, the data makes clear the times and locations that need to be watched.
This project assessed crime affecting children, including close calls, and recorded children's daily activities in terms of both time and location, and developed methods for proposing / evaluating countermeasures adapted for the circumstances surrounding the crime and the characteristics of the community and residents. It collected crime data and built a portal site for sharing the information.
The project also held workshops in communities, reported on case studies that led to improved crime prevention, and featured in the fiscal year 2011 white paper on science and technology.
Training Program for Video Recorded Interview (Forensic interviews) with Children in Forensic Context (FY2008-2012)
Principal Investigator: NAKA Makiko (Professor of Graduate School of Letters, Hokkaido University)

Right: A role play of an interview with a child participant
Left: Learning forensic interviewing techniques
Successfully acquiring a testimony from a child when he or she witnesses to or is affected by a crime is the key to securing the child's safety and preventing reoccurrences, but it had been believed extracting the facts without giving the child leading questions was very difficult.
Therefore, this project developed and gave training on forensic interviewing techniques for extracting high-quality information usable in court and other judicial situations by encouraging children's free narratives and by recording and videotaping interviews, while minimizing the burden on children as much as possible.
Development of Support Systems for Community Safety Planning (FY2008-2012)
Principal Investigator: YAMAMOTO Toshiya (Professor, Department of Science and Technology, Meiji University)

Community safety inspection by children
A portal website was developed for this project in order to support community safety planning (planning of a community which is easy to live in for both children and adults and is safe and comfortable in terms of crime prevention). It includes an e-manual collecting know-how and examples of planning, implementing, evaluating and improving, and provides municipalities nationwide with information on community safety planning. Not only manuals but also Web examinations and an analysis tool of questionnaire results are available on the portal website.
In 2011, this project established the "Community Design Partners for Children's Safety" to promote support for the comprehensive activities for safe and comfortable community planning.
Development of Advanced Information and Simulation Technology for Intentional Injury Prevention (FY2008-2012)
Principal Investigator: YAMANAKA Tatsuhiro (Director, Injury Prevention Engineering Research Team (IPERT), Digital Human Research Center, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology)
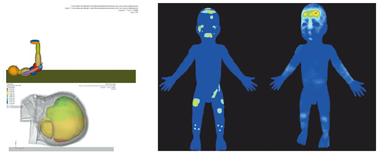
Left:Technology for biomechanical simulation of attacks and accidents
Right:Development of injury database: Frequency of injury in cases where abuse is suspected (left) and frequency of injury caused by accidents (right).
This project developed support tools for use at child welfare centers, hospitals and so on to determine whether an injury was intentional (the result of abuse, etc.) or accidental. We developed simulation technology that uses test dummies to reproduce situations in which injuries occur, injury data acquisition and storage systems using maps of the human body, and software tools to support the process of determining whether there has been abuse. These systems have been used to aid actual police investigations.z
R&D Focus Area: Science Technology and Humanity
Establishment of the "Science Media Centre of Japan" as an Information Hub for Science and Technology (FY2009-2012)
Principal Investigator: SEGAWA Shiro (Professor, Faculty of Political Science and Economics, Waseda University)

Left: Science Alerts published on the SMC website
Right: SMC's international network reports the return to earth of JAXA's asteroid explorer, Hayabusa
Today, the news is full of information about science and technology. This project established the Science Media Centre of Japan (SMC Japan) to create an intermediary communication setup between science and the media. During the aftermath of the Great East Japan Earthquake, when there were still ongoing incidents such as the nuclear disaster, the SMC acted quickly to collect comments from a variety of experts and made them available to the media as scientific perspectives. It also introduced the media to these experts directly. SMC is working to provide a new system for facilitating debate in today's post-industrial society.
Construction of a Pragmatic Scientist Community Contributing to the Stakeholder-driven Management of the Local Environment (FY2008-2012)
Principal Investigator: SATO Tetsu (Professor, Center for Coordination, Promotion and Communication, Research Institute for Humanity and Nature)

Left: Examples of local communities participating in LSNES. In 2012, it started to expand into an international network
Right: Field workshop on Ishigaki-jima
Even when a scientifically appropriate solutions to local environmental problems are proposed, it is sometimes not accepted by local communities. This could be due to discrepancies between scientific knowledge production and values, problem structures and decision-making systems inherent to particular local community.
Therefore, this project formed the Local Science Network for Environment and Sustainability (LSNES) as a platform for residential researchers who conduct research as stakeholders of local communities and for knowledge translators and stakeholders in the communities throughout the country. LSNES provides guidelines for collaboration between scientists/experts and various local stakeholders and is developing participatory evaluation systems of local science with stakeholders.
The Nagahama Rules for Genome Epidemiology Studies Open to the Community (FY2007-2012)
Principal Investigator: AKASHI Keiko (Section Sub-leader, Nagahama City Health and Welfare Division Health Promotion Section)

Residents participating in the research established the NPO Zeroji (Pre-primary prevention) Health Promotion club, which plays an important role in improving citizens understanding for the research by such way as producing a regular project information magazine.
Genome data is said to be the ultimate personal information. Consequently, it is vital for the whole of society to give serious consideration to the ethics and to the issue of how to protect personal information in R&D projects that handle genome data. This project is associated with a genome epidemiology project conducted through collaboration between Nagahama City and Kyoto University ("Nagahama Zeroji Cohort Project for Community-based Prevention"). The RISTEX project attempted to emphasize the perspectives of the Nagahama citizens participating in the research, and for that purpose formulated the "Nagahama Rules" concerning the storage, management, and utilization of samples. The Cohort Project is a long-term project that aims to promote R&D using the genome, and to build a healthy community--it has only just begun.
Legal Decision-making under Scientific Uncertainty (FY2009-2012)
Principal Investigator: NAKAMURA Tamiko (Lawyer, Lybra Law Office)

Left: Lawyers, scientists, students, and members of the public join in discussions at workshops and a Cafe for Law and Science Philosophy
Right: The Law and Science Handbook
This project was established to consider what sort of setup would lead to better judicial decisions based on a correct understanding of the fact that science and technology always involve uncertainty. Through this project, practicing lawyers and scientists collaborated to clarify fundamental issues such as what is a trial, what is science, and why do discrepancies occur between the law and science.
The project's findings have been summarized in a "Law and Science Handbook" designed for lawyers and scientists involved for the first time in a case involving science. The handbook helps lawyers and scientists to understand each other and provides hints for how to conduct discussion between them.
Implementation-Support Program
Practical Utilization of Multi-dimensional Scale for PDD and ADHD (MSPA) across the Medical, Education and Social field: FY2014-2017
Principal Investigator : FUNABIKI Yasuko (Associate Professor, Graduate School of Human and Environmental Studies, Kyoto University)
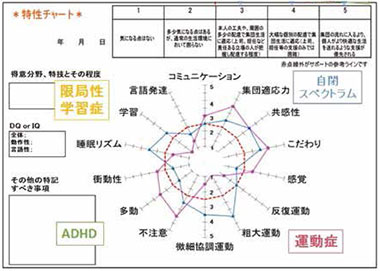
There are various symptoms associated with developmental disabilities, and these can vary tremendously between individuals. Thus, we put into practical use an assessment scale (MSPA: Multi-dimensional Scale for PDD and ADHD) that assesses in details the level of support required and displays the results with a radar chart for individuals with developmental disabilities and their supporters to grasp easily. We formulated a manual to support the assessment for each life stage of people with developmental disabilities, developed a program for the training of evaluators, and engaged in the training of experts by regularly holding training sessions. In addition, our activities related to the proposal of this assessment method to be included in medical insurance bore fruit, and it became insurance-covered in April 2016, which leads to the social implementation of a comprehensive support system.
Co-creating Communities for Aged Society: FY2016-2018
Principal Investigator: TSUJI Tetsuo (Professor, Institute of Gerontology, The University of Tokyo)

The complexity of the challenges posed by an aging society means that they cannot be solved by a one-size-fits-all approach. Rather, such challenges require a response tailored to the characteristics of each local community. This implementation project targeted two neighborhoods with different local characteristics in Kashiwa City, Chiba Prefecture, and was aimed at creating a framework for local residents to take the initiative in addressing local issues. Based on the results of these activities, we proposed two implementation approach models for solving such issues: the "policy collaboration model" and the "local accumulation model." Furthermore, during the project period, the Co-creation Center for Active Aging (now the Co-creation Center for Future Society) was established as a general incorporated association. The Center continues to present case studies, encourage networking and conduct other implementation activities across Japan that will contribute to addressing the challenges of an aging society.
A joystick system to enable people with disabled limbs to drive a car: FY2011-2014
Principal Investigator: WADA Masayoshi (Associate Professor, Institute of Engineering, Graduate School, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology)

Long-Standing Tsunami Response and Education Activities Result in "Miracle of Kamaishi" (Establishing a Foothold for Nationwide Expansion of Tsunami Education Using a Comprehensive Tsunami Disaster Scenario Simulator: FY2008-2012)
Principal Investigator: KATADA Toshitaka (Professor, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Gunma University)

Children heading to safety on the day of the disaster. Older children led younger children by the hand to keep them moving
It has long been seen as a major problem that many people do not sufficiently appreciate the risk of a tsunami and do not evacuate even when a tsunami warning is issued. Professor Toshitaka Katada of Gunma University, working in the RISTEX R&D Focus Area of Safety and Security, developed the Comprehensive Tsunami Disaster Scenario Simulator, which has proven useful for promoting resident evacuation and for consideration of disaster prevention measures by local governments. Since then, Professor Katada, under the Implementation-Support Program, had used the simulator to pursue disaster prevention education activities for residents of the town of Mugi in Tokushima Prefecture, Miyakojima in Okinawa Prefecture, and several other locations vulnerable to earthquake and tsunami damage.
At one place where Professor Katada had pursued this work, Kamaishi City in Iwate Prefecture, the tsunami that struck as a result of the Great East Japan Earthquake was much larger than planned for in disaster preparation. Despite that, however, 2,926 children, 99.8% of the city's whole elementary and junior high school students were successfully evacuated in what is now called the "Miracle of Kamaishi."
Community-based System for Early Identification and Intervention of Toddlers with Autism Spectrum Disorder, whose Item Incorporated in Maternal and Child Health Handbook (Social Implementation of an Early Intervention System for Children with Developmental Disorders and Their Families: FY2009-2012)
Principal Investigator: KAMIO Yoko (Director of Department of Child and Adolescent Mental Health, National Institute of Mental Health, National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry)

Learning tool for professionals deployed using e-learning
Early identification of children with autism spectrum disorder, and early intervention to children and their families, promotes the child's social development, and improves social participation and quality of life of the child, his or her family, and for society as a whole.
Dr. Kamio's team has been involved in the Brain Science & Society R&D area, conducting a community-based cohort study over a five year period in conjunction with a local government. The researchers were able to develop and implement an early identification and support system for infants with a typical social development who need support.
Since fiscal year 2009, the results of this research have been deployed under the RISTEX Implementation Support Program, to aim to enhance the skills of primary health professionals such as health nurses and pediatricians, so that they can appropriately evaluate child's development, provide childcare advice, and refer to specialized centers. To enable early identification of children requiring support systematically, these professionals created support network to exchange systematic knowledge and practical clinical experiences using e-learning tools, which contributed to prevail the community-based early support system. In fiscal year 2012, when the Maternal and Child Health Handbook was revised for the first time in ten years, the important item related to early social development was incorporated as a checkpoints at checkup for one-year-old children .
Development of Predictive System to Prevent Trailer Truck Rollover (Rollover Prevention System of Trailer Truck for Contributing to Safer Logistics and Secure Society: FY2008-2011)
Principal Investigator: WATANABE Yutaka (Professor, Faculty of Marine Technology, Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology)

Gyroscope unit for system predicting trailer truck rollover limit speed
Trailer trucks transporting freight containers have special issues with the characteristics of the truck body due to the load in the container potentially being off-center or having a high center of gravity. As a result, even when traveling within legal speed limits, there is substantial risk that the vehicle may be unable to negotiate a curve safely without rolling over. Recent accidents resulting from such circumstances have involved ordinary people who happened to be at the scene of the accident.
Working in the Social Systems/Science and Technology for Society research area, Professor Watanabe and his team analyzed the causes of trailer truck rollover and developed a system that could prevent accidents by predicting the limit speed at which negotiating a curve result in a rollover, and warning the driver.
Since fiscal year 2008, the outcomes of this research have been actively deployed under the RISTEX Implementation Support Program, using test drive sessions and talks to raise awareness, and also exhibiting at trade shows and taking other measures expected to lead to wider adoption of the technology. The response, both domestic and international, has been large and positive.
This issue has attracted a great deal of attention from society at large, and has also led to new legislation being enacted and brought into force, requiring owners importing freight to inform truck companies and drivers of the container content, weight, and other information.
Development and Introduction of Systems for Providing Life Recovery Support Measures Rapidly and Fairly after a Major Disaster (Development of Life Recovery Support System for a Possible Tokyo Metropolitan Earthquake: FY2010-2013)
Principal Investigator: Haruo HAYASHI (Professor, Research Center for Disaster Reduction Systems, Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University)/ TAMURA Keiko (Professor, Risk Management Office, Headquarters for Risk Management, Niigata University) * succeeded since 2012

Left: Practice at issuing Disaster Victim Certificates at Tokyo Metropolitan Government's comprehensive disaster drill facility in September 2012
Right: Professor Haruo Hayashi describes the system to Naoki Inose, then vice governor of Tokyo Metropolitan Government
After a major earthquake or other disaster, local authorities provide Life recovery supports in the form of monetary support to the people affected, helping them to rebuild their lives. However, that process requires lists of eligible people to be compiled. Systems designed for use in normal circumstances are unable to cope smoothly after a disaster, and there is the issue that there has been no verification of effectiveness or of information security concerning privacy information and similar data.
Professor Hayashi and his team, working in the Information Technology & Society research area, have developed systems capable of issuing Disaster Victim Certificates much more rapidly than conventional approaches enabling people to receive Life recovery support measures smoothly immediately after the disaster, but still maintaining information security.
Since fiscal year 2010, this research has continued under the RISTEX Implementation Support Program, conducting demonstrations and customizations required in order to deploy the systems. In addition to being used in places such as Otsuchi-chou, Iwate prefecture, after the Great East Japan Earthquake, the researchers are collaborating with Tokyo to customize the systems to work with Metropolitan Tokyo's own systems with the aim of being able to distribute Life recovery support rapidly, fairly, and without omissions in the event of Tokyo Metropolitan near-field earthquake which exceeds M7, as is predicted. These systems are already being introduced in the Toshima ward and Chuo ward in Tokyo as well as Kyoto city.
Microbubbles Clean Seawater, Bringing Hope to Aquaculture Producers in the Tsunami Zone (Water Purification in Closed Water Area and Recovery of Aquaculture by the Use of Large-Scale Microbubble Generators: FY2011-2012)
Principal Investigator: OONARI Hirohumi (Professor, National Institute of Technology, Tokuyama College)

Microbubbles produce plump, juicy oysters
Ofunato Bay was famous for its oyster farms before the disaster, but since then there have been problems with shellfish toxin and red tides, and water quality has declined. Under the Implementation-Support Program for Urgent Implementation of Support in Response to the Great East Japan Earthquake, this project has used compact low-power microbubble generators to clean the water, thereby assisting the livelihood of local aquaculture producers. Beginning in early August 2011, 104 microbubble generators were installed in the Takonoura area of Ofunato Bay, running them 24-hours a day until February 2012. By providing a source of good quality oxygen and nitrogen, after three and a half months, oysters had grown to about twice their usual size.
A great deal of equipment had been lost in the tsunami, including aquaculture rafts, boats, and other facilities, and some of the producers had lost their own homes, too. The damage was so substantial that many producers were giving up oyster farming. However, this project gave them hope by demonstrating a potential way to recover the Akasaki oysters that had been a well-known premium before the disaster. In addition to installing similar devices at locations such as Kesennuma and Kamaishi, progress is being made with a new JST Revitalization Promotion Program.
Development and Deployment of Web System to Support Children and Their Parents Contributes to the Quality Improvement of Childcare Professionals (Web-based Support System for Child Care: FY2010-2013)
Principal Investigator: ANME Tokie (Professor, Faculty of Medicine, University of Tsukuba)

Childcare professional tries out the support system using a tablet computer
At a time when birthrates have decreased and the population is aging, parents with young children are increasingly likely to feel lonely, anxious, and overburdened. There are also a growing number of children who need special care due to developmental disorders or other factors, and society's expectations for support from nursery staff and other professionals involved in childcare are increasing. At the same time, many professionals are unsure how to distinguish problem behavior in children, identify children requiring special consideration at an early stage, detect signs in parents, or provide quality support in collaboration with other organizations.
This project has deployed the five tools for childcare professionals based on scientific evidence from a 12-year nationwide cohort study. The tools are a general development assessment tool, a social skills scale, a child's home environment assessment tool, a childcare environment assessment tool, and a support tool for children that raise concerns. They have been developed as web applications delivered from a cloud-based platform, and are being deployed using table computers.
Other Major R&D Achievements funded by RISTEX
Electronic Critical Path System (Study on application of manufacturing safety methods to medical accident prevention: FY 2002-2005)
Principal Investigator: NOGUCHI Hiroshi (Professor, Faculty of Engineering, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Kyushu University)
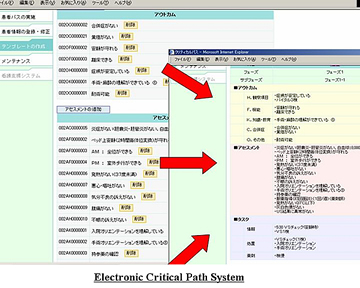
- indicates all or part of a patient's case record and care plan, developed and used by a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals
- for the team to follow its content and thus to manage their task forces while reducing medical accidents
- in use at Kyushu University Hospital
Tailor-made Computer Simulations (Mission Program I "Building a knowledge system for solving social issues related to safety": FY 2001-2005)
Principal Investigator: KATADA Toshitaka (Professor, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Gunma University)
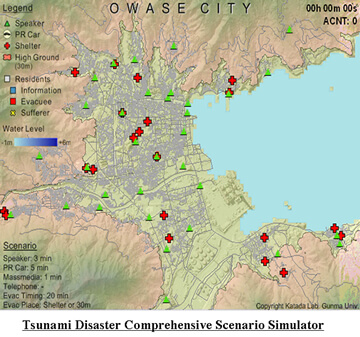
- examines the effectiveness of disaster prevention plans for tsunami by visualizing economic/human losses
- factors in various elements (e.g., timing) of evacuation orders as well as the data for a particular local area (e.g., population, geography, history of tsunami damage)
- is under development or already in use by a number of cities as a planning and educational tool
Self-evaluation Tool for Organizations (Development of indicator, methodology and information disclosure of environmental rating: FY 2001-2004)
Principal Investigator: FUKUSHIMA Tetsuro (Adviser, Japan Audit and Certification Organization for Environment and Quality (JACO))
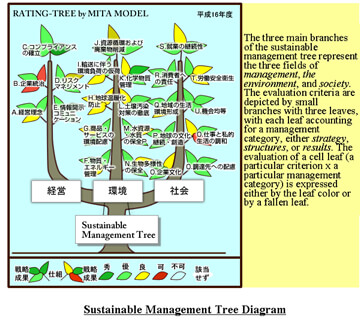
- rates efforts in environmentally-aware management work
- visualizes levels of [1], management, [2], environmental protection and [3], social responsibility in a tree diagram
- utilized by Sustainable Management Forum of Japan as well as many private and public organizations
Learning/Therapy Curricula (R&D in development of prefrontal cortex functions development and improvement systems: FY 2001-2004)
Principal Investigator: KAWASHIMA Ryuta (Professor, Institute of Development, Aging and Cancer, Tohoku University)
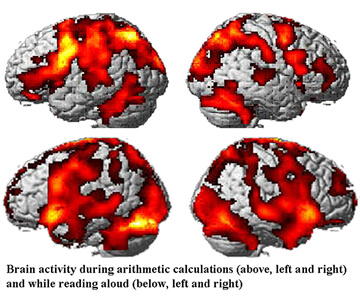
- treats dementia and improves social communication skills of elderly patients
- revitalizes prefrontal functions of patient brains through recitation and simple-arithmetic exercises
- adopted by 712 facilities with approx. 9,000 users nationwide (as of March 2008)
Support Programs/Network Systems for Children with Learning Disabilities (CLD) using an E-learning System (Elucidation of brain mechanisms of learning difficulties and development and evaluation of educational support programs: FY 2003-2006)
Principal Investigator: MASATAKA Nobuo (Professor, Primate Research Institute, Kyoto University)
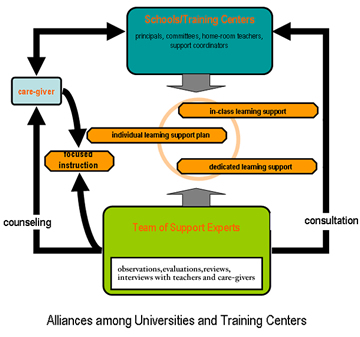
- based on comprehensive evaluations of the level and specifics of individual learning disabilities of children (i.e., through systematic medical examinations)
- helps CLD through consistent use of e-learning materials at multiple locations
- fosters collaboration among the families, schools and communities of CLDs
- currently being implemented in Nagoya and Kyoto cities.
Multiple Risk Communicator (Multiple risk communicator working group: FY 2003-2007)
Principal Investigator: SASAKI Ryoichi (Professor, Engineering Department, Tokyo Denki University)
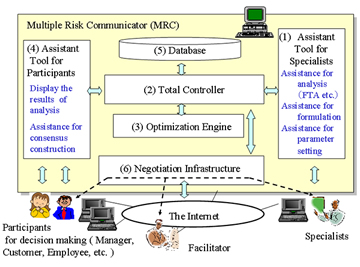
- consists of an optimization engine (computing part) and a negotiation infrastructure (opinion exchange tool among stakeholders and specialists)
- helps to build consensus among decision-makers by drawing the optimal combination of measures based on information regarding various risks and costs in information security as provided by stakeholders and specialists
- officially adopted by 95 elementary and junior high schools in Setagaya-ku Tokyo
Social Experiment to cope with Nagoya City's Waste Problems (A Study for Realization of Environmentally Sound Material-Cycle Society Based on Citizen's Participation: FY 2002-2005)
Principal Investigator: YAGISHITA Masaharu (Professor, Institute for Studies of the Global Environment, Sophia University)
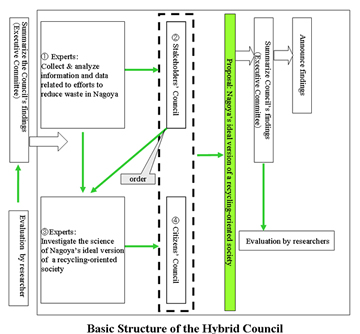
- involved 3 parties: [1], stakeholders (i.e., local government, private sector), [2], experts, and [3], citizens, in a new framework for a decision-making method which was formally adopted by the city
- the framework's policy recommendation (on the directions and ideas for the city as a recycling oriented society) was implemented as Nagoya's waste management policy