R&D Projects
Development of Methods for Impact Assessment of Electric Power Innovation and R&D Network Evaluation
Project Director

- AKIYAMA Taro
Professor, Center for Economics Growth Strategy,
Yokohama National University
<Project Homepage>
Development of Methods for Impact Assessment of Electric Power Innovation and R&D Network Evaluation
Objective
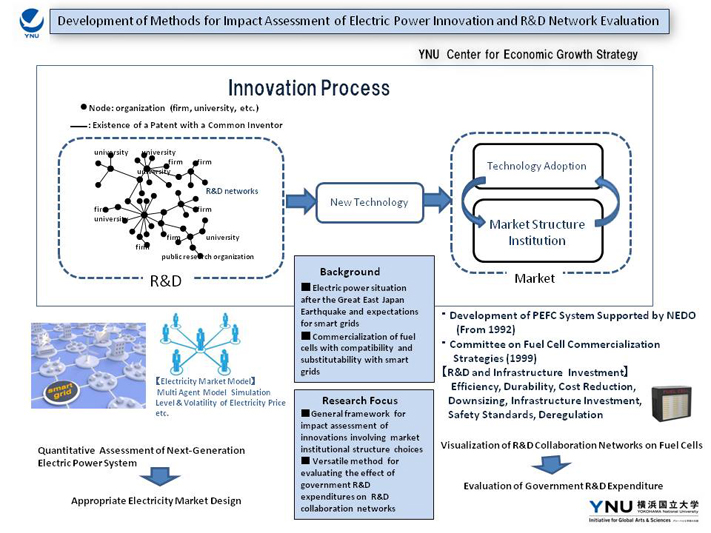
The contents of the project are as follows. First, we will carry out a quantitative impact assessment of next-generation electric power systems, taking choices of market and institutional structures into account, and contribute to appropriate electric power market design. Secondly, we will estimate a R&D collaboration network of fuel cell technologies, and use the results to evaluate government R&D expenditure on fuel cells.
By carrying out of the assessment and evaluation of advanced technologies in electrical power-related fields, we will develop a general framework for impact assessment of innovation which involves changes in market and institutional structure, and develop a versatile method for evaluation of the effects of government R&D expenditure on R&D collaboration networks.
Outline
The background to this problem can be summarized in the following three points.
- (1)Due to the electric power situation aggravated by the Great East Japan Earthquake, it is widely acknowledged that the introduction of smart grids will be an effective way to reduce electric power uses, especially for peak demand.
- (2)Technological improvements of fuel cells make it possible to use them as distributed generators in smart grids. On the other hand, fuel cells can be used as off-grid electric power supply systems. The rapid spread of off-grid electric power supply systems may have an adverse impact on the introduction of smart grids.
- (3)In addition to the debate on smart grids after the Great East Japan Earthquake, electric power market reform has become an urgent problem. The impact of introducing smart grids depends on the electricity market structure and institutions.
Therefore, to solve the current problems in electricity market reform, innovations in power systems such as smart grids as well as choices for the market and institutional structure should be taken into account. However, there are no such impact assessment of the next-generation power system taking into account appropriate market and policy systems in Japan. Furthermore, there is a tendency to focus on the compatibility between smart grids and fuel cells, but the possible effect of a competitive relationship between grids and fuel cells has not been taken sufficiently into account. Finally, there have been several studies concerning R&D evaluation in the field of fuel cells, but there are no studies from the perspective of R&D collaboration networks despite huge government R&D expenditure in these fields.
In view of these factors, this project concentrates on innovation in smart grids and fuel cells, and aims to study the following subjects which will contribute to an electric power innovation policy:
- )Taking the choices of appropriate market and institutional structures into account, assess quantitatively the impact of electric power system innovation by smart grids and fuel cells, and design an appropriate electricity market based on this assessment
- )Estimate R&D collaboration networks on fuel cells, and evaluate government R&D expenditures on fuel cell technologies from the perspective of R&D collaboration networks
Based on the results of the project, the general framework for assessing the impact of innovation, which involves choices of market and institutional structure systems such as infrastructure, and a versatile method for evaluating the effects of government R&D expenditure on R&D collaboration networks will be developed. These will greatly contribute to science, technology, and innovation policy.