Advanced and Sustainable Methods on Water Utilization Associated with Greening Potential Evaluation
Environment / Energy (Global-scale environmental issues)
 Republic of Djibouti
Republic of Djibouti
Principal Investigator


Dr.
President of University of Djibouti
Djama Mohamed Hassan
ODA Recipient Country
Republic of Djibouti
Research Institutions in Japan
Tokyo University of Agriculture / Kansai University / The University of Shimane / Kyoto University /Geosphere Environmental Technology Corp. / Oriental Consultants Global Co.,Ltd.
Research Institutions in Counterpart Country
University of Djibouti / Center for Studies and Research of Djibouti / Ministry of Agriculture, Water, Fisheries, Livestock and Marine Resources of Djibouti
Adoption fiscal year
FY 2018
Research Period
5 Years
Overview of the Research Project
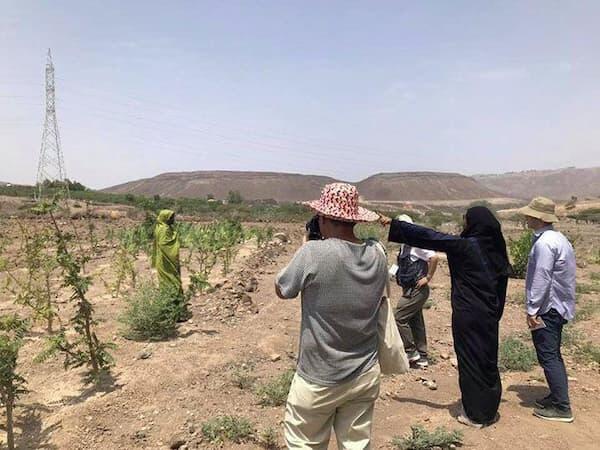
Assessing water resources/greening potential and demonstrating agropastoral practices
Most of Djibouti is a harsh desert environment, and the country’s food self-sufficiency ratio is only about 13 percent by value. This project aims to ascertain the distribution, circulation pathways, and sustainable usage levels of Djibouti’s water resources over a wide area and from a three-dimensional perspective, and expand the area where agropastoral practices are used. Satellite images and UAV images taken throughout Djibouti are used to assess the current situation based on the relationship between water resources and greening potential/sheep farming potential. The project also aims to propose water-saving agropastoral models as an extension of the oasis farming model by developing useful plants and feed crops, along with greening through effective use of urban waste.
Making efficient use of water resources to enhance arid areas by greening wasteland and by creating agropastoral land
This project aims to identify optimal areas for greening and to extend the use of sustainable agropastoral practices suitable for arid lands by conducting demonstrations at suitable locations. The process involves determining the circulation of water in Djibouti as a whole, and, by extension, groundwater flow systems throughout Africa, and identifying other arid lands with potential for implementation of the techniques.
Photo gallery
Research Project Web site
Press Release
Links
Projects
Contact Us
Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST)
Department of International Affairs
SATREPS Group
TEL : +81-3-5214-8085
Related articles by Category
- Global-scale environmental issues
Environment / Energy
(Global-scale environmental issues)
 Kingdom of Thailand
Kingdom of Thailand
“Natural rubber seeds”, the unlimited potential hiding in natural rubber plantations
Utilization Technology of Rubber Seeds for Green Products to Mitigate Global Warming and Plastic Pollution
- Africa
Environment / Energy
(Global-scale environmental issues)
 Republic of Zambia
Republic of Zambia
Experienced, not taught - Realizing safe water, sanitation and hygiene in Africa
Risk-based Participatory WASH Planning and Citizen-data WASH Statistics for African Peri-urban Settlements
- SDGs : Goal.2
Bioresources

 Republic of Indonesia
Republic of Indonesia
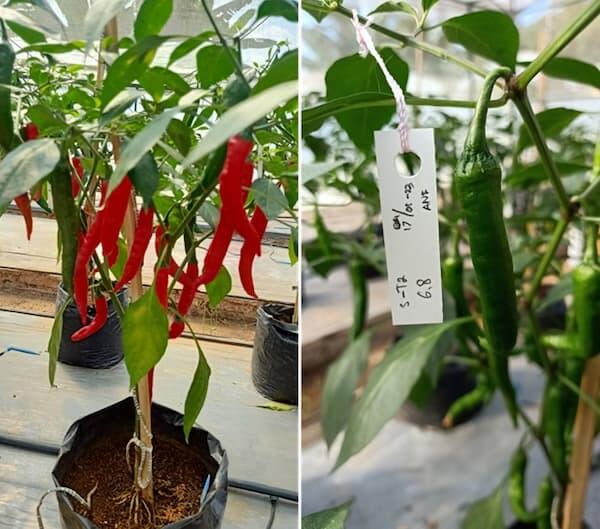
Achieve sustainable vegetable production in tropical regions using advanced breeding technology!
Breeding Innovation in Chili Pepper and Tomato to Accelerate Sustainable Vegetable Production in Tropical Regions























