
Kapybara3D
Masaaki MIKI, Lifeng Zhu, Jun MITANI, Takeo IGARASHI
Abstract
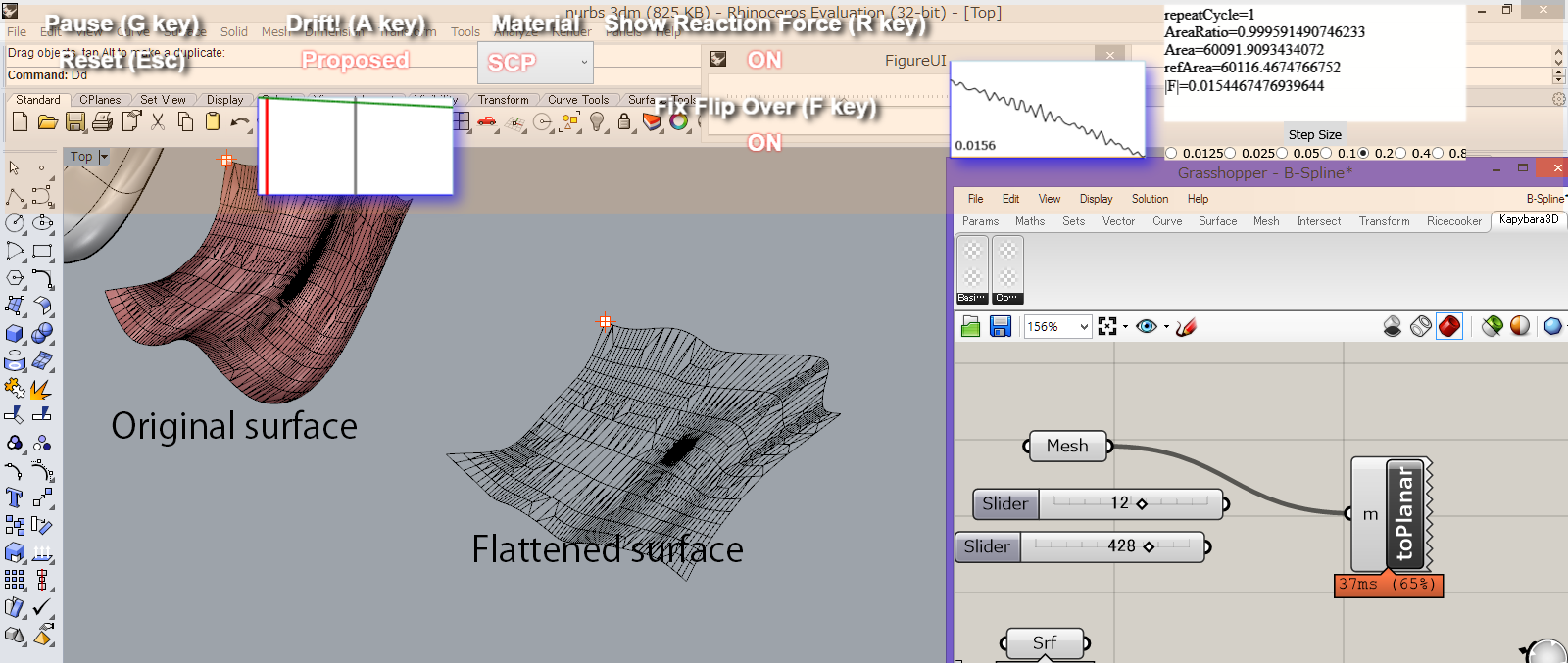
The Rhinoceros® is a Nurbs specialized comercial CAD modeler and the Grasshopper is an Add-on of the Rhinoceros® that allows users to visually define sequential rules to generate complex geometries by simply connecting components. The combination of the Rhinoceros and the Grasshopper is now booming in the field of architectural design and expected to bridge the gap between designers and engineers such that total number of users is rapidly increasing in both buisiness and education. We have been developing Kapybara3D, which is a set of custom components of the Grasshopper that provides us multiple solutions of surface flattening. In surface flettening, a flattened surface that is nearest to the reference surface is expected but an objective measure of the "nearest" is not unique except developable surfaces. Hence, a user must choose an appropriate measure, that is, energy functional, that is suitable for each particular purpose from the given list of choices. We investigated a number of existing parameterization methods and picked out several methods that are clasified as surface flattening. Then, we re-expressed the energy functionals in a common and standerized manner. Additionally, we derived stress tensors from the energy functionals by introducing a viewpoint of continuum mechanics and explicitly expressed them in terms of first fundamental forms. The major characteristics of implementation of our components is that methods are switched between by just switching between the stress tensors. Except computation of stress tensors, all computations are standerized by common subroutings based on the nonlinear finite element method.
Videos
Switching methods by switching stress tensors
Publications
Masaaki MIKI, Lifeng Zhu, Jun MITANI, Takeo IGARASHI, Stress Tensors in Surface Parameterizations, Oct21-23, MEIS2013, Fukuoka, Japan,
![]()









