Progress Report
Development of “Jizai Hon-yaku-ki (At-will Translator)” connecting various minds based on brain and body functions[2] Interpreting mental states through exosomes
Progress until FY2024
1. Outline of the project
In R&D Item 2, we develop technologies to evaluate our mental states through exosomes in our body fluid. Information of mental states will be provided to Jizai-hon-yaku-ki system, and used to optimize the quality of communication aids.
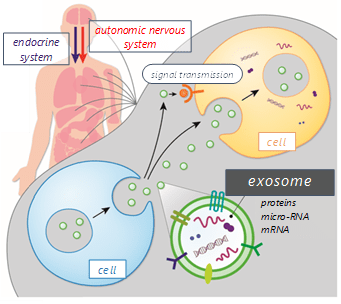
Our body fluid (like saliva and blood) contains small particles, exosomes, produced in cells of various organs. One of their functions is to manage metabolic waste. But they also have another interesting role — intercellular communication. Increasing attention has been paid to this function of exosomes, as they might work as biomarkers of bodily and neurodegenerative diseases.
It is pointed out that the uptake of exosomes into the brain is connected to (changes in) the state of the brain. However, little is known about the relationship between one’s exosomes and mental state.

Source: https://www.rcast.u-tokyo.ac.jp/ja/research/people/staff-hoshino_ayuko.html
Our R&D Item 2 aims to unravel the interactions of the brain and other organs mediated by exosomes through bio-chemical examinations and AI-based data analysis.
2. Outcome so far
- Social stress induces profound changes in brain and gut exosomes
- Discovered differences in exosome-containing protains between individuals with ASD and Neurotypical Individuals
- Establishment of a new measurement and analysis system for investigating mouse social and other behavioral characteristics
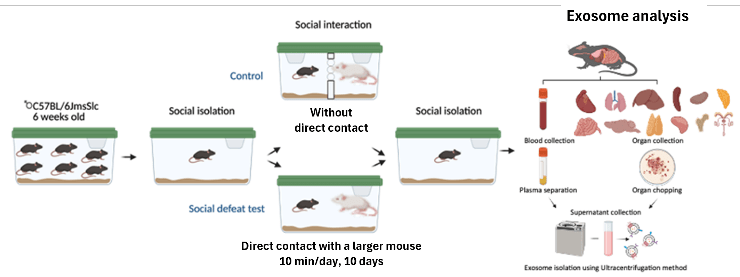
Outcome 1: Using mice, we found that exposure to social stress dynamically changes blood exosomes, in particular the composition of exosomes derived from the brain and gut. This result is highly anticipated as a clue to explore the relationship between exosomes and mental state.
Outcome 2: We analyzed the protein composition contained in exosomes from individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and Neurotypical individuals. As a result, we found that there were differences in complement molecules, which are related to immunity, and that machine learning using 24 of these molecules makes it possible to diagnose ASD with high accuracy.
Outcome 3: We established a system to record the location and identify individual mice housed in groups and analyze their behavioral characteristics. We hope to identify good exosome indicators related to behavioral characteristics using this sysmte.
We are advancing basic research to unravel the interactions between exosomes and brain function.
3. Future plans
Our R&D Item 2 will further investigate the interactions of brain and other organs mediated by exosomes. Furthermore, we aim to develop technology to interpret mental states multidimensionally by integrating information from exosomes with brain activity and othe physiological signals (R&D Item 1).
(U Tokyo: A. Hoshino, A. Nasiri Kenari)