News & Topics
“Research Development on K-Ion Batteries” published in ACS Chemical Reviews
A-STEP
https://www.jst.go.jp/a-step/kadai/h28-s1/h28_senryaku01.html
SICORP
https://www.jst.go.jp/inter/english/program_e/multilateral_e/concert-japan.html
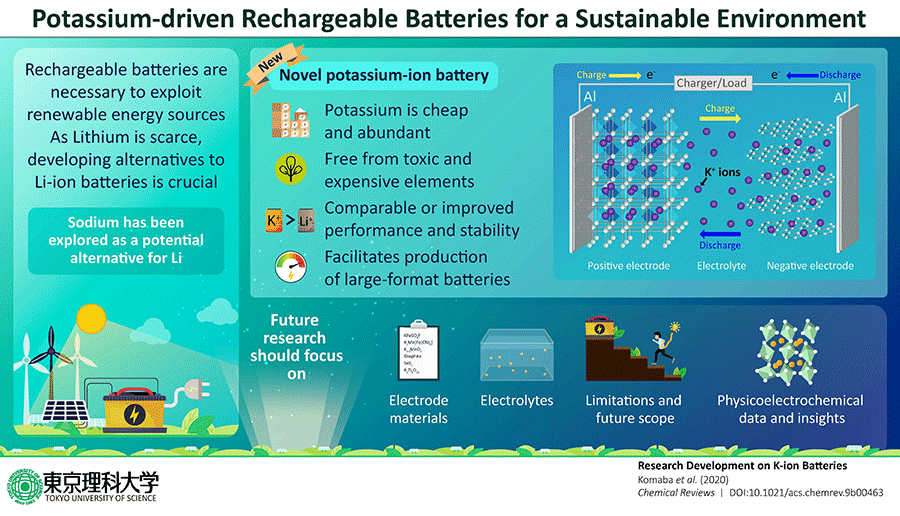
A Tokyo University of Science research team led by Professor Komaba Shinichi and Junior Associate Professor Kubota Kei published a comprehensive review of K-ion batteries (KIBs), a type of battery widely expected to become a popular alternative to lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), in ACS Chemical Reviews on January 15.
Compared with LIBs, not only are the materials necessary for building KIBs cheaper, but KIBs are also expected to be safer while simultaneously drawing a comparable voltage to LIBs.
In 2015, Prof. Komaba, et al. demonstrated how a high-performance charge and discharge reaction progressed in an electrolyte containing potassium ions using graphite negative electrodes on a board of aluminum foil, a finding which was eventually published in an academic journal. Subsequently, the team succeeded in developing a new type of secondary battery which exhibits the same 4-volt class voltage as LIBs by using Prussian blue analogues, of which the main components are iron and manganese, which had been developed as a positive electrode in previous research. Moreover, the team discovered that potassium exhibited faster ionic diffusion in electrolytes compared with lithium or sodium. As a result, the output was improved and an excellent rapid charge and discharge capability was exhibited, a research result eventually published in 2017.
The review, titled “Research Development on K-Ion Batteries,” covers previous research on electrolytes, positive and negative electrodes, and all sorts of materials including trace additives for lithium-, sodium-, and potassium-ion batteries. It covers various synthesis methods, their physical properties and the performance of each element when applied to batteries. This article is the first comprehensive review that compares all the potential solutions that can be used for electrolytes and positive and negative electrodes.
For more detail, visit the Tokyo University of Science Website:
https://www.tus.ac.jp/en/mediarelations/archive/20200115001.html
- Funding information
- In addition to JST's programs mentioned below, this study was partly funded by the MEXT program "ESICB" (Grant Number JPMXP0112101003) and JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Numbers JP16K14103, JP16H04225, and JP18K14327).
JST Programs
- Adaptable and Seamless Technology Transfer Program through Target-driven R&D (A-STEP)
- Research Theme: Creation of New Technologies for Next-Generation Energy Storage System Supporting High Efficient Energy Use
(Program Officer: Kanamura Kiyoshi, Professor, Tokyo Metropolitan University)
Research Project: R&D on fundamental technologies for potassium ion batteries and potassium ion capacitors
(Project Leader: Komaba Shinichi, Professor, Tokyo University of Science)
- Strategic International Collaborative Research Program(SICORP) EIG CONCERT-Japan
- Research Area:Efficient Energy Storage and Distribution
(Program Officer: Domen Kazunari, Special Contract Professor, Shinshu University)
Research Project:Low-Cost and Efficient Sodium-Ion Battery Based on Abundant Elements(LIBRA)
(Research Leader in Japan: Komaba Shinichi, Professor, Tokyo University of Science)
- Journal Information
- Journal: Chemical Reviews, published on January 15, 2020
- Title: “Research Development on K-Ion Batteries”
- Authors: Tomooki Hosaka,1 Kei Kubota1,2, A. Shahul Hameeda1,2, and Shinichi Komabaa1,2
1. Department of Applied Chemistry, Tokyo University of Science
2. ESICB, Kyoto University - DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00463