Progress Report
Towards overcoming disorders linked to dementia based on a comprehensive understanding of multiorgan network[1-4] Brain and multi-organ network in Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia and Parkinson’s disease dementia (1)
Progress until FY2024
1. Outline of the project
The three major diseases responsible for dementia are Alzheimer’s disease (AD), vascular dementia (VD), and Parkinson’s disease (PD)-related dementia (including Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB)). This section aims to elucidate the inter-organ connections (organ crosstalk) during the preclinical phase of these types of dementia by utilizing cutting-edge model mice and human cohorts such as the MAAB cohort, J-PPMI cohort, and the Nagahama cohort, through the application of mathematical analysis and other advanced techniques. The ultimate goal of this research is to develop predictive methods for risk assessment and to establish preventative interventions to delay or prevent disease onset.
This study uses model mice that accumulate disease-causing proteins and later develop irreversible symptoms, allowing analysis before onset. Similarly, human cohorts focus on individuals in the pre-symptomatic stage.
- AD Group Lead: Koji Yamanaka (Nagoya Univ)
- VD Group Lead: Naoki Mochizuki (National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center)
- PD Group Lead: Nobutaka Hattori (Juntendo Univ)
- Basic Technology Group Lead: Toshihisa Otsuka (Yamanashi Univ)
2. Outcome so far
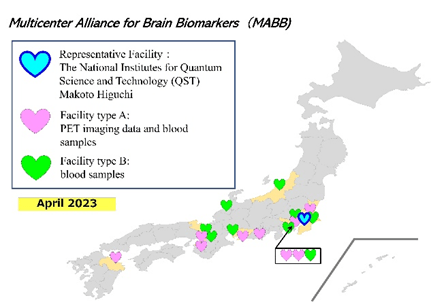
A multicenter preclinical cohort for dementia
The MABB preclinical cohort for dementia, involving 18 institutions, is a multicenter initiative promoting the development of imaging and blood biomarkers. A key feature is the secondary use of data and samples from other clinical studies, accelerating biomarker validation.
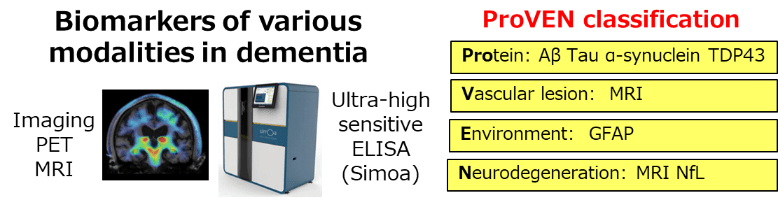
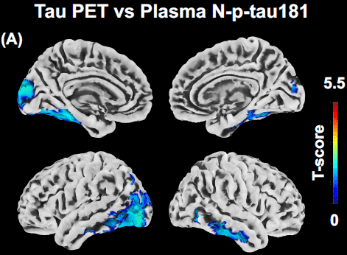
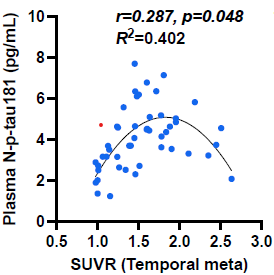
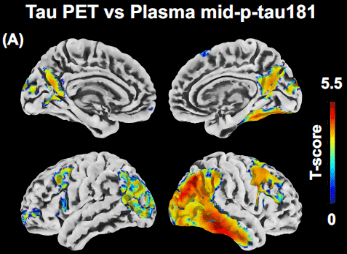
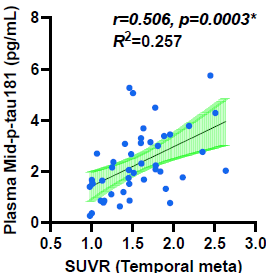
Our group focuses on the ProVEN classification, a comprehensive approach to dementia subtyping that analyzes pathological proteins (Protein), brain inflammation (Environment), vascular lesions (Vascular), and neurodegeneration (Neurodegeneration) using biofluid biomarkers, MRI, and PET. Notably, a new high-sensitivity assay has successfully detected blood phosphorylated tau, a key Alzheimer’s biomarker, correlating with neuronal damage (Transl Neurodegener, 2024).
Novel PET Tracer for Visualizing α-Synuclein (αSyn)
PD and DLB are characterized by the pathological aggregation of the protein α-synuclein (αSyn), which leads to neuronal cell death. Although a PET tracer capable of visualizing aggregated αSyn has long been sought after, Dr. Masato Higuchi and his team at the National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology have become the first in the world to develop such a tracer. This innovation has enabled the detection of pathological lesions in PD and DLB patients (Neuron, 2024).

3. Future plans
Various types of data will be collected from original disease models and preclinical cohorts for dementia. Furthermore, we will identify candidate biomarkers that contribute to early diagnosis through data-driven analysis of multi-organ networks and try to predict and prevent the development of dementia.