Collision of localized traveling convection cells in binary fluids
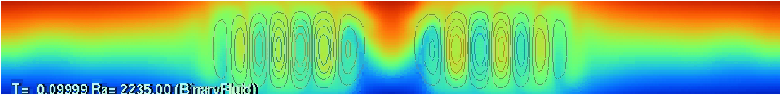
We study the collision processes of spatially localized convection cells (pulses) in a binary fluid mixture by the extended complex Ginzburg-Landau equations. Both counter- and co-propagating pulse collisions are examined numerically. For counterpropagating pulse collision, we found a special class of unstable time-periodic solutions that play a critical role in determining the output after collision. The solution profile right after collision becomes close to such an unstable pattern and then evolves along one of the unstable manifolds before reaching a final destination. The origin of such a class of unstable solutions, called scattors, can be traced back to two-peak bound states which are stable in an appropriate parameter regime. They are destabilized, as the parameter is varied, and become scattors which play the role of separators of different dynamic regimes. Delayed feedback control is useful to detect them. Also, there is another regime where the origin of the scattors is different from that of the above case. For co-propagating pulse collision, it is revealed that the result of pulse collision depends on the phase difference between pulses. Moreover, we found that the coalescent pulse propagates while maintaining a two-peak bound state, which is not observed in the case of counter-propagating pulse collision. Complicated collision dynamics become transparent to some extent from the viewpoint of those unstable objects.
[1]M. Iima and Y. Nishiura: "Collision of localized traveling-wave convection cells in binary fluid", GAKUTO International Series, Mathematical Sciences and Applications, 22: 289-303 (2005)
[2]M. Iima and Y. Nishiura:"Unstable periodic solutions controlling collision of localized convection cells in binary fluid mixture, submitted.

