Research Results
First Practical Application of Deep Fake Video Detection Technology in Japan
SYNTHETIQ VISION, Automatic Evaluation of the Authenticity of AI-Generated Fake Facial VideosFY2025

- ECHIZEN Isao (Director, Global Research Center for Synthetic Media, National Institute of Informatics)
- CREST
- Research Director (2020-2025), Trusted quality AI systems Area: "Social information technologies to counter infodemics"
- A-STEP
Principal Investigator (2021), Establishment of Technologies to Detect Fake Media of AI-Generated Facial Videos, Tryout project
- YAMAGISHI Junichi (Deputy Director, Global Research Center for Synthetic Media, National Institute of Informatics)
- CREST
- Research Director (2018-2023), Symbiotic Interaction Area: "VoicePersonae: Speaker identity cloning and protection"
Automatic evaluation of the authenticity of "avatars" of celebrities and other prominent figures
SYNTHETIQ VISION: Synthetic video detector, a program for automatic evaluation of the authenticity of AI-generated fake facial videos, which was developed by a research team led by Director Isao Echizen and Deputy Director Junichi Yamagishi of the Global Research Center for Synthetic Media, National Institute of Informatics (NII), has been used by CyberAgent, Inc. to detect deep fake*1 videos of celebrities and other prominent figures since 2023.
From 2021, CyberAgent has been offering Digital Twin Label, a service that produces official 3D computer graphic models as "avatars" of prominent figures such as celebrities and artists for use in events and commercials or as apparel models in the cyberspace. This business decided to implement SYNTHETIQ VISION to prevent the production and dissemination of deep fake videos by ill-intended third parties that replace the face of the "avatar" with other faces or modify it.
This implementation is Japan's first case of applying technologies for automatic authenticity evaluation of AI-generated fake face videos to an existing service.
*1 Deep fake
A coined term that combines the terms deep learning and fake. Refers to fake media including fake images, fake videos, fake audios, and fake documents that are synthesized in a real-looking manner using AI with malicious intent.
Long awaited highly accurate technology that distinguishes "real" and "fake"
Synthetic media has become possible by having AI learn large amounts of human face, voice, language, and other data to produce facial videos, audios, and writing that can be mistaken for being real. There is high anticipation for synthetic media technologies*2 for broad use in engineering simulations, new artistic expressions, and in the entertainment sector to enhance our society and lives.
On the other hand, it poses the risk of malicious third parties producing deep fakes (fake media), such as real-looking videos and audios, in order to commit fraud, break through facial and voice recognition systems, and spread fake news that would cause social disruption. In fact, cases of fake information being disseminated in the cyberspace using fake images and voices of celebrities have become a social problem, and there is a need for the advancement of technologies that can discern "real" and "fake” for authenticity evaluation in order to prevent such problems.
*2 Synthetic media technology
Synthesis technology that produces realistic voices, images, and videos using AI.
SYNTHETIQ VISION, enabling companies that employ the system to easily and swiftly evaluate authenticity
NII has been advancing research to protect the rights of digital content, including the digital watermarking technology, which prevents illegal copying and alteration by embedding special information in digital data such as images, videos, and audios.
SYNTHETIQ VISION was developed based on the outcomes in two CREST research area themes and by leveraging A-STEP program.
The speaker identity cloning and protection research developed a high-precision speech synthesis technology while also working to develop new technologies that strengthen voice security measures and privacy protection. The unique aspect is that the research team employed an "adversarial competitive research" approach, in which the researchers separated into the offensive side and defensive side and competed. Through such approach, the research team enhanced the level of technologies for safety enhancement in speaker authentication systems, protection of privacy, and automatic protection against voice impersonation attacks (Fig. 1).
In the social information technologies to counter infodemics*3 research, the research team developed technologies for automatic detection and prevention of attacks using fake videos, audios, and documents in order to address potential threats posed by fake media, as well as to establish reliable social information fundamental technologies that support diverse communication and decision making in the cyberspace.
Both research teams have been advancing the development of deep learning*4 models to evaluate the authenticity of fake audios and videos as common basic research. This evaluation method automatically distinguishes based on a large volume of data and does not require any human analysis. Another characteristic feature of the system is that it can evaluate with a certain degree of reliability even for media whose quality has deteriorated due to information compression or low resolution.
To implement these results into society, in 2021, the research team developed the fake media detection application SYNTHETIQ VISION as a software package that can be easily incorporated into other applications, with the support of A-STEP program (Fig. 2). With SYNTHETIQ VISION, the entire process, from the server uploading of videos subject to authenticity evaluation to the downloading of evaluation results, can be performed automatically, enabling companies that implement the software to easily and quickly evaluate authenticity.
*3 Infodemics
A coined term that combines information and epidemic, which refers to the rapid increase of infections within a limited region. A phenomenon in which a mixture of uncertain and certain information spreads rapidly online and through other social media.
*4 Deep learning
Deep learning is a collective term that refers to multiple independent machine learning methods. A method of learning that associates information on a subject matter from the overall picture to the details in a hierarchical structure.
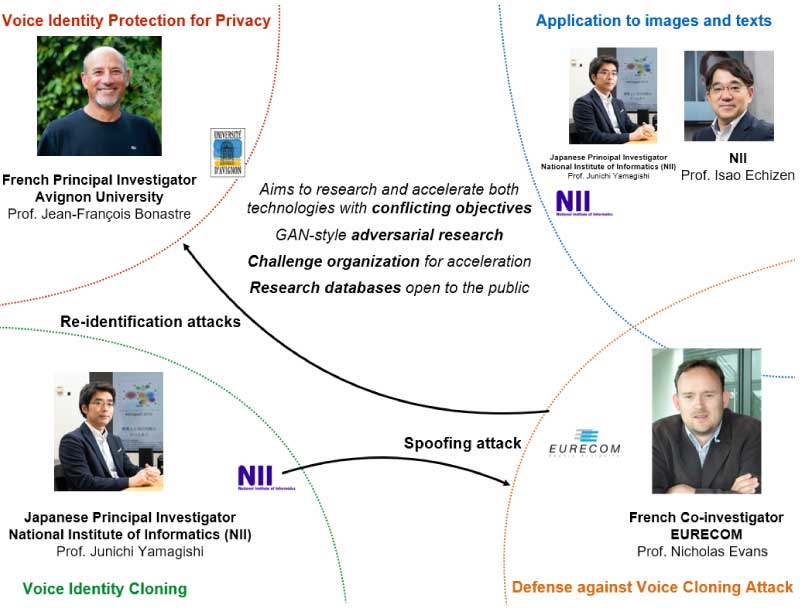
Fig.1 Project Scheme for Speaker Identity Cloning and Protection
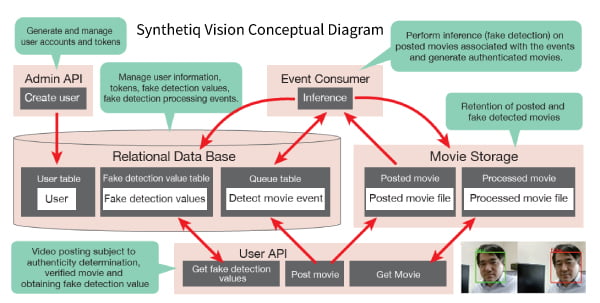
Fig.2 Conceptual Diagram of SYNTHETIQ VISION (source: NII Today, volume 100)
To broad use in the prevention of malicious fake media
SYNTHETIQ VISION was licensed to several companies in 2023, and CyberAgent announced that it will use the software for authenticity evaluation in its "Digital Twin Label." This is Japan's first case of applying automatic authenticity evaluation technology for AI-generated fake facial videos to an existing service. The implementation of a service in society that companies can easily implement and quickly check facts is of great significance. Going forward, it is expected that SYNTHETIQ VISION will be widely employed by businesses including financial institutions, online communication providers, the entertainment industry, social media, news media, and forensics providers.
Additionally, NII which developed SYNTHETIQ VISION, will participate and play a key role in the project announced in October 2024 on the development of a disinformation countermeasure platform, a project including Fujitsu Ltd. and nine industry-academia organizations.
