Progress Report
Elucidation of the mechanism of serotonin over optimism and pessimism[1] Serotonin subsystem for optimism and pessimism: observation and measurement
Progress until FY2024
1. Outline of the project
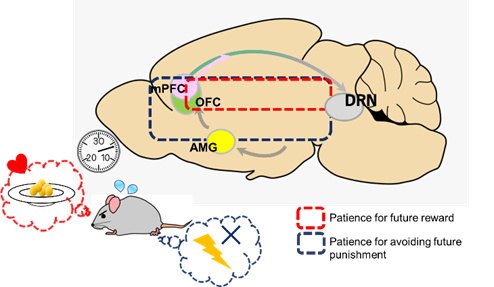
In this research topic, we focus on the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN), which is the nucleus origin of serotonergic neurons, and the medial prefrontal cortex, orbitofrontal cortex, and amygdala, which are the projection sites of serotonergic neurons. These brain regions are known as the neural substrates that organize action selection and decision-making based on sensory input and are important for generating our mind. We use invasive methods (fiber photometry, fluorescence microscope camera), which are difficult for human studies, for observation of neural activity in real time during reward acquisition or punishment avoidance behavior.
2. Outcome so far
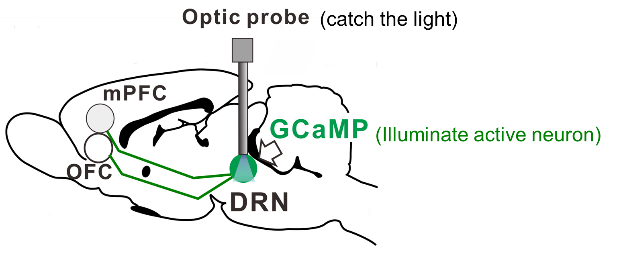
1.1 Observation of serotonergic activity in the DRN
In this study, we observed serotonin neural activity during mice performing a reward waiting task in which reward probability is changed from 25% to 100%. Serotonin neurons show increased activity during waiting for future reward and phasic increased activity to food presentation. We found that serotonin neural activity during waiting periods is modulated by reward probability. This discovery was made possible by combining the latest experimental techniques with behavioral tasks based on our original hypothesis, and is attracting attention from engineering and medical fields as a new role for serotonin.
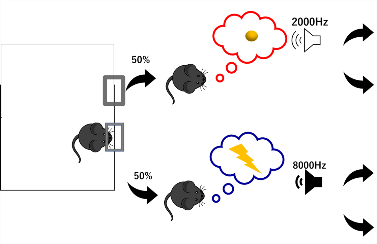
We also introduced reward acquisition/punishment avoidance task in which mice can acquire food in the future by waiting for a few seconds in a designated area (waiting excitedly) or avoid a weak foot shock (waiting helplessly because they do not want to feel pain). From the outside, mice seem to behave in the same way, but the purpose in their minds is different depending on the conditions. We are now observing serotonin neural activity in the DRN under each of these conditions.
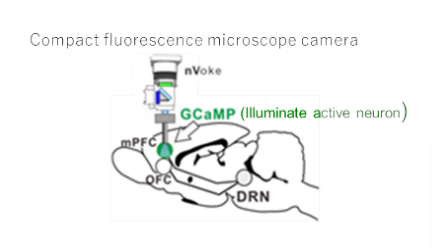
1.3 Observation of neural activity in the brain region of serotonin projection
With fluorescence microscope camera, which weighs about 2 g and is attached to mouse's head, we observed hundreds of neural activities in orbitofrontal cortex and medial prefrontal cortex while the mouse performed the reward waiting task. Many neurons responded while waiting for delayed reward suggesting that they may be strongly influenced by serotonin input.
3. Future plans
We will clarify how serotonin neuronal activity in the DRN is expressed depending on whether the goal is to obtain reward or avoid punishment. Using a compact fluorescent microscope camera, we will clarify how the orbitofrontal cortex and medial prefrontal cortex neurons respond during the reward acquisition/punishment avoidance tasks.
(MIYAZAKI Katsuhiko, MIYAZAKI Kayoko, OIST)