Research Results
Pioneering the First Novel Radiotherapeutic from Japan
Advancing the Development and Commercialization of the First-Ever Japanese Cancer RadiotherapeuticFY2025

- YOSHII Yukie (President & CEO, LinqMed Inc.; Senior Researcher, Institute for Quantum Medical Science, National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology until December 2023)
- START
- Principal Investigator (2020-2022), Project Promotion Type "Technological Development for Commercialization of Innovative Cancer Radiotherapeutics"
Advancing the clinical implementation of next-generation radiotherapeutics
Senior Researcher Yukie Yoshii and colleagues at the Institute for Quantum Medical Science, National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology have been using the copper radioisotope 64Cu to develop a next-generation radiotherapeutic that is highly effective in treating malignant tumors and can simultaneously diagnose and treat cancer.
With the aim of implementing this next-generation radiotherapeutic into clinical practice, Senior Researcher Yoshii founded LinqMed Inc. on July 1, 2022. This venture company specializes in the development and marketing of this next-generation radiotherapeutic with the support of the Program for Creating STart ups from Advanced Research and Technology (START) by the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST).
Among the radiotherapeutics under the development, LinqMed has initiated a Phase 3 randomized controlled clinical trial of 64Cu-ATSM for the treatment of recurrent and refractory malignant brain tumors. This study is the final stage of clinical trials, and this agent is expected to be approved as the first-ever Japanese radiotherapeutic.
Innovative "visible" cancer radiotherapeutics with 64Cu
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy for cancer have seen challenges including insufficient therapeutic effect and adverse reactions associated with damage to normal cells. Senior Researcher Yoshii et al. hypothesized that the copper radioisotope 64Cu could potentially overcome these challenges and have been working to develop radiotherapeutics using 64Cu.
In addition to the beta rays emitted by nuclides used in conventional radiotherapeutics, 64Cu emits a specific type of radiation called Auger electrons.*1 Auger electrons have the remarkable feature of being able to effectively treat cancer cells with high energy. Additionally, since 64Cu also emits positrons, it can be used for positron emission tomography (PET) diagnosis. Leveraging these attributes, 64Cu can be bound to the drug accumulating on cancer cells in order to treat the cancer while noninvasively confirming drug accumulation on the cancer (treatment with simultaneous visualization) (Fig.1).
LinqMed is committed to bringing its innovative "visible” cancer radiotherapeutics based on the distinct properties of 64Cu to clinical practice as quickly as possible. This breakthrough has the potential to overcome refractory cancers with no effective treatment options, enable personalized therapies tailored to the condition of each patient's cancer, and optimize medical care that simultaneously assessing adverse reactions.
*1 Beta rays, Auger electrons
Beta rays generally exhibit a maximum range in the millimeter range and are used in conventional radiopharmaceuticals. Since Auger electrons generally exhibit a short maximum range in the nanometer scale, they can apply high energy in their immediate vicinity, which is generally considered to result in high therapeutic efficacy.
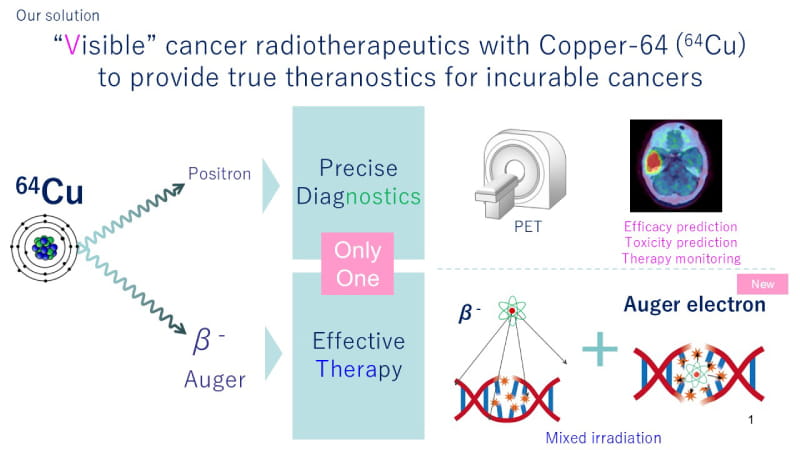
Fig.1 Innovative “Visible" cancer radiotherapeutics with 64Cu Cancer is the leading cause of death, and recovery from refractory cancers that have no other treatment methods require innovative diagnostic and treatment options. LinqMed is committed to deliver efficient and optimal medical care through "visible" cancer radiotherapeutics with 64Cu, which can be used for both diagnosis and treatment.
The first-ever first-in-human clinical trial of a radiotherapeutic developed in Japan
LinqMed has initiated a Phase 3 randomized controlled clinical trial of its investigational agent 64Cu-ATSM as a radiotherapeutic for recurrent or refractory malignant brain tumors (Fig.2).
The treatment options have been insufficient for patients with malignant brain tumors, and further drug development has been urgently required. The hypoxic tissue microenvironment plays a key role in the poor prognosis of brain tumors. In conventional radiation therapy, radiation exposure generates reactive oxygen species (ROS), which damages the DNA of cancer cells and promotes cell death. However, hypoxia occurs in relapsed malignant brain tumors, and reduces ROS generation and making radiation therapy less effective.
To overcome these challenges, Senior Researcher Yoshii and her colleagues developed 64Cu-ATSM, which accumulates into the hypoxic tumor cells and exhibits high therapeutic efficacy. In preclinical studies using cancer cell xenografted mice, Senior Researcher Yoshii et al. confirmed that 64Cu-ATSM suppresses the growth of hypoxic malignant brain tumors and improves survival rates. Encouraged by these promising findings, this agent has been developed as a radiotherapeutic for malignant brain tumors. LinqMed is committed to bring this innovative technology into clinical practice as promptly as possible.
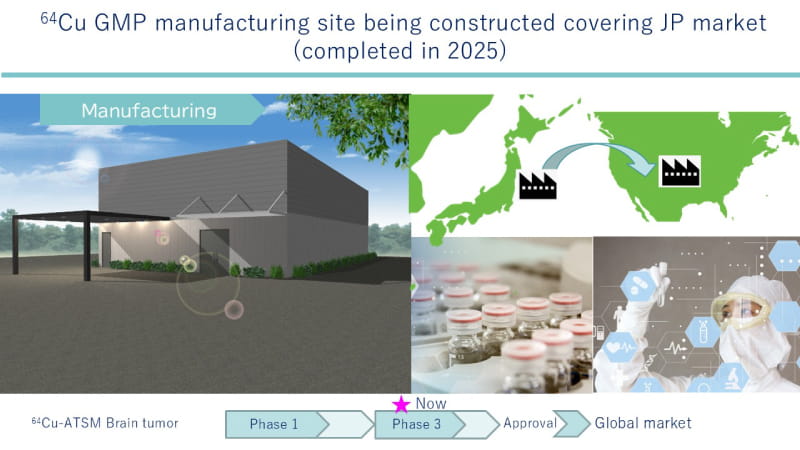
Fig.2 Roadmap of 64Cu-ATSM towards clinical practice Focusing on the fact that refractory cancers including malignant tumors become hypoxic, LinqMed is developing a novel radiotherapeutic, 64Cu-ATSM, which allows treatment of hypoxic refractory tumors with simultaneous visualization. LinqMed is committed to implement this agent into clinical practice as a 64Cu therapeutic as quickly as possible.
LinqMed’s commitment to innovative "visible" cancer treatment
Cancer is the leading cause of death in Japan, and the development of new diagnostic and therapeutic options is an urgent issue. LinqMed has been using the copper radioisotope 64Cu to develop next-generation radiopharmaceuticals that can be used for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in cancer. We are constructing a 64Cu GMP manufacturing site in Japan to produce 64Cu for the Japanese market.
In addition to 64Cu-ATSM, which targets recurrent or refractory malignant brain tumors, LinqMed is developing both diagnostic and therapeutic 64Cu-agents for pancreatic cancer. Furthermore, several drug discovery programs targeting solid tumors, such as bile duct cancer, are underway. LinqMed is dedicated to continuously developing 64Cu-based radiopharmaceuticals for various clinical applications and contributing to the acceleration of technological innovation in Japan.
- Life Science
- Research Results
- Japanese
