

Brief Summary of the Symposium:
The primary most common cause of the death of children aged from 1 to 19 years of age is a "mishap", and not only in Japan but also other advanced countries. The focus at the International Symposium on Everyday Life Computing for Injury Prevention was on the issue of "preventing injuries occurring from accidents", something that has been attracting growing interest both domestically and internationally, and speakers reported on global trends in the area of injury prevention and the latest achievements in relation to everyday life computing technologies being used to solve the injury problem. This was the first time the international symposium for injury prevention was held in Japan.
Accident prevention is difficult firstly because individual accidents are associated with differing complicated phenomena. From as academic perspective that prevention requires behavioral clarification of a complicated system that is made up of the development of the cognition and behavior of children, the development of the cognition and behavior of their guardians, and the wide range of products found in our day-to-day living environments. It cannot be clarified only by professionals working in limited disciplines, with instead the complicated system calling for an interdisciplinary research framework. Secondly, accident prevention on a societal basis cannot be achieved without the cooperation of a diverse range of organizations, which include medical, research, industrial, governmental and legislative organizations.
"Basic Technology Research on Sensing and Computational Theory of Everyday Life Behavior for Injury Prevention", which falls within the research area of "Advanced Integrated Sensing Technology", by the JST CREST has been developed sensing technology for use with everyday life behavior, and modeling technology that utilizes large-scale data collection and simulation technology, in an effort to establish basic technologies for injury prevention since October 2005. In addition, it has been promoting activities in the creation of safe communities while conducting studies on the practical application of the developed technologies in accident prevention. The symposium was held to provide an opportunity for high level presentations and discussions to take place from both the angle of technological needs and social needs, and accelerate initiatives to create interdisciplinary research communities and various cross-sectional cooperation through presentation of reports on the activities of the WHO, who are promoting injury prevention, the trend with research in countries that are taking a progressive approach to injury prevention, and the accident prevention engineering technologies being developed within JST CREST.
At the symposium four foreign speakers from WHO, the Johns Hopkins University in the U.S., Monash University in Australia, and The University of Alabama in U.S. all made presentations in connection with global trends in area of injury prevention. Three presentations from domestic speakers addressed the approach to injury prevention in Japan, engineering techniques, and other topics. The symposium was participated in by 106 people involved in a variety of fields from universities, public research institutes, local governments, educational institutes, corporations, an incorporated nonprofit organization (NPO) promoting safe child design, the news media and other bodies. Since the symposium was being held in Japan and participated in by many non-researchers simultaneous interpretations were provided to facilitate the understanding of participants from the general public.
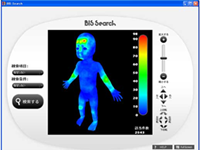
After the presentation session an open house at the facility researching injury prevention promoted by the JST CREST was held to demonstrate a drowning prevention sensor developed for use in bathrooms, a bodygraphic information system (downloadable at http://www.cipec.jp/#/project/) and others. The bodygraphic information system was revealed to the public free of charge on the date of the symposium. The system that was released to the public enables users to access a database of about 4000 cases of accidents amassed from hospitals, and to then view at a glance a color coded bodygraphic image of, for example, that "tea, coffee and miso-soup" mishaps cause burns mostly to the left thigh, right chest and right arm. The content of the international symposium and the software released to the public were covered by the media, including newspapers, and TV and radio stations.


For more information on the programs etc please view the following website.