Exosome engineering
Exosomes as nanocarriers for systemic delivery of the Helicobacter pylori virulence factor CagA
| Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) CagA protein is known as a risk factor of gastric mucosa disorder, while the relationship with extragastric diseases has not been proven. In this study, we found that exosomes containing CagA were released from H. pylori CagA-expressing cells and retained its biological activity. We also found that CagA was detectable within exosomes from the blood of individuals infected with cagA-positive H. pylori. These results suggested that H. pylori CagA-containing exosomes may be involved in the development of multiple extragastric diseases. | 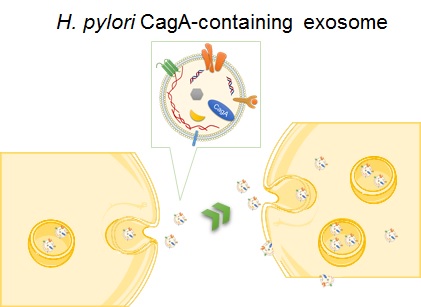 Fig.1 Systemic delivery of the H. pylori CagA by exosomes. |
| Paper A. Shimoda, K. Ueda, S. Nishiumi, N. Murata-Kamiya, S. Mukai, S. Sawada, T. Azuma,M. Hatakeyama, K. Akiyoshi, Exosomes as nanocarriers for systemic delivery of the Helicobacter pylori virulence factor CagA Scientific Reports, in press. |
Engineering hybrid exosomes by membrane fusion with liposomes
| Exosomes are a valuable biomaterial for the development of novel nanocarriers as functionally advanced drug delivery systems. To control and modify the performance of exosomal nanocarriers, we developed hybrid exosomes by fusing their membranes with liposomes using the freeze–thaw method. Exosomes embedded with a specific membrane protein isolated from genetically modified cells were fused with various liposomes, confirming that membrane engineering methods can be combined with genetic modification techniques. Cellular uptake studies performed using the hybrid exosomes revealed that the interactions between the developed exosomes and cells could be modified by changing the lipid composition or the properties of the exogenous lipids. | 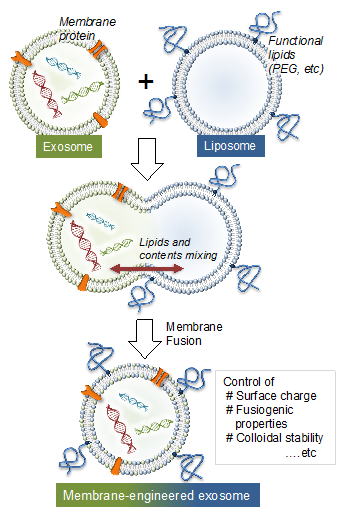 Fig.1 Schematic of method used to engineer the exosome–liposome hybrids. |
| Paper Y.T. Sato, K. Umezaki, S. Sawada, S. Mukai, Y. Sasaki, N. Harada, H. Shiku and K. Akiyoshi, Engineering hybrid exosomes by membrane fusion with liposomes. Scientific Reports. 6, 21933; doi: 10.1038/srep21933 (2016). |
